HRMP Channels¶
Introduction¶
Polkadot is designed to enable seamless interoperability between its connected parachains. At the core of this interoperability is the Cross-Consensus Message Format (XCM), a standard language that allows parachains to communicate and interact with each other.
The network-layer protocol responsible for delivering XCM-formatted messages between parachains is the Cross-Chain Message Passing (XCMP) protocol. XCMP maintains messaging queues on the relay chain, serving as a bridge to facilitate cross-chain interactions.
As XCMP is still under development, Polkadot has implemented a temporary alternative called Horizontal Relay-routed Message Passing (HRMP). HRMP offers the same interface and functionality as the planned XCMP but it has a crucial difference, it stores all messages directly in the relay chain’s storage, which is more resource-intensive.
Once XCMP is fully implemented, HRMP will be deprecated in favor of the native XCMP protocol. XCMP will offer a more efficient and scalable solution for cross-chain message passing, as it will not require the relay chain to store all the messages.
Establishing HRMP Channels¶
To enable communication between parachains using the HRMP protocol, the parachains must explicitly establish communication channels by registering them on the relay chain.
Downward and upward channels from and to the relay chain are implicitly available, meaning they do not need to be explicitly opened.
Opening an HRMP channel requires the parachains involved to make a deposit on the relay chain. This deposit serves a specific purpose, it covers the costs associated with using the relay chain's storage for the message queues linked to the channel. The amount of this deposit varies based on parameters defined by the specific relay chain being used.
Relay Chain Parameters¶
Each Polkadot relay chain has a set of configurable parameters that control the behavior of the message channels between parachains. These parameters include hrmpSenderDeposit, hrmpRecipientDeposit, hrmpChannelMaxMessageSize, hrmpChannelMaxCapacity, and more.
When a parachain wants to open a new channel, it must consider these parameter values to ensure the channel is configured correctly.
To view the current values of these parameters in the Polkadot network:
-
Visit Polkadot.js Apps, navigate to the Developer dropdown and select the Chain state option
-
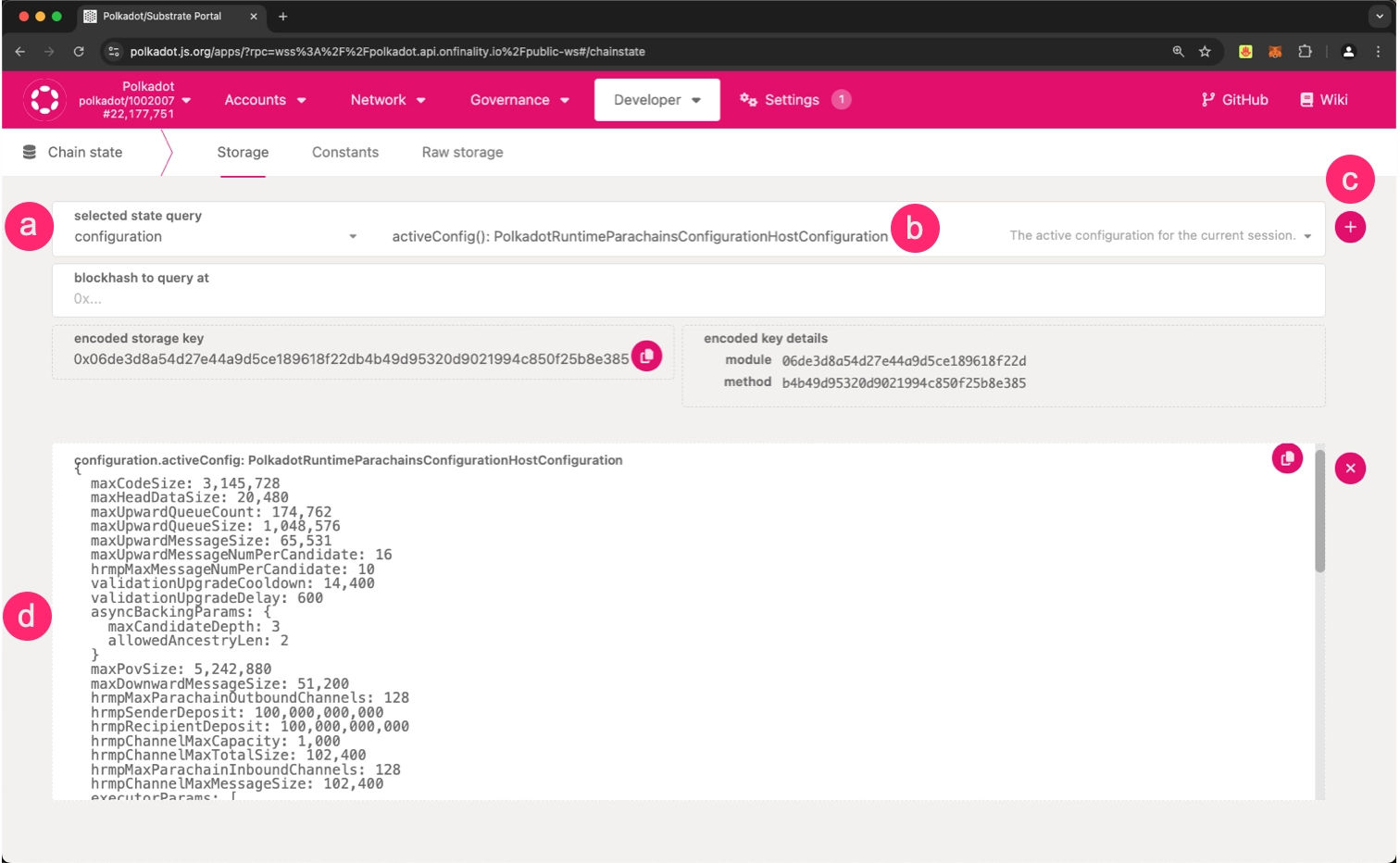
Query the chain configuration parameters. The result will display the current settings for all the Polkadot network parameters, including the HRMP channel settings
- Select configuration
- Choose the activeConfig() call
- Click the + button to execute the query
- Check the chain configuration
Dispatching Extrinsics¶
Establishing new HRMP channels between parachains requires dispatching specific extrinsic calls on the Polkadot relay chain from the parachain's origin.
The most straightforward approach is to implement the channel opening logic off-chain, then use the XCM pallet's send extrinsic to submit the necessary instructions to the relay chain. However, the ability to send arbitrary programs through the Transact instruction in XCM is typically restricted to privileged origins, such as the sudo pallet or governance mechanisms.
Parachain developers have a few options for triggering the required extrinsic calls from their parachain's origin, depending on the configuration and access controls defined:
- Sudo - if the parachain has a
sudopallet configured, the sudo key holder can use the sudo extrinsic to dispatch the necessary channel opening calls - Governance - the parachain's governance system, such as a council or OpenGov, can be used to authorize the channel opening calls
- Privileged Accounts - the parachain may have other designated privileged accounts that are allowed to dispatch the HRMP channel opening extrinsics